>> DNS HACKING <<
1 DNS BASICS
2 RESOURCE RECORDS AND THE ZONE FILE
3 DNS LOOKUP AND REVERSE DNS LOOKUP
4 DNS ZONE TRANSFER
5 WHY SECURITY ISSUE OF ZONE TRANSFERING
6 CONCLUSION
1 Dns Basics:- DNS converts human readable domain names into IP-addresses. This is because domain names are much easier to remember than IP-addresses. This process may take place through a local cache or through a zone file that is present on the server. A zone file is a file on the server that contains entries for different Resource Records (RR).
This process can be understand by this example let’s assume that you write in URL bar of browser “www.google.com” the this query first goes to DNS server their resolve the site name in Ip address and then goes to query for web page of google com to web. server.
It’s not easy task to remember every IP address of various web site. so there DNS resolver work to resolve website name into IP address .
Ex. (Generally all people stored phone no. by particular person’s name ) .
2 resource records and zone file:- A zone file is basically a text file that contain the information of records and hosted on hosting server .
There are some DNS record listed here
A - NS record (name server )
B – Host A record [ipv4]
C - Host AAAA record [ipv6]
D – SOA [start of authority record]
E – MX record [mail exchanger record]
F – CANNONICAL NAME record [Alias of one name to another]
G – SRV record [service record]
H – PTR record [pointer]
NSLOOKUP is a dns quering tool that can be used to resolve ip address from domain name or vice-versa . this tool is used to query any given name server for specific records..
For DNS query using nslookup utility in first typing the nslookup quickly it show the default sever as I m using rcomwlnsmum.rilinfo.net which provided by the ISP automatically.
And now changing the default server by typing server 8.8.8.8 . This is publicly available domain name server provided by google. it is beneficial to have listing of several publicly available DNS server when performing your testing . And useful to check of sort when dealing with a compromised DNS server .
In query of resources record type “ set type=a” for ip address record.
Query for name server record type “set type=ns”
Query for mail exchanger type “ set type=mx”
As shown in image can see all type of DNS resources record which are entries of zone file.
3> DNS lookup and reverse lookup:-
DNS Lookup-Let’s perform a DNS Lookup We will do this by traversing the entire DNS hierarchy from the root servers to the top level domain. Open up the terminal in Backtrack and type in “dig”. You will get something as shown in the figure below.
What we get is a list of the Root DNS Servers. Let’s use this root DNS server to query indianrail.gov.in. as shown in image
What we get is a list of authoritative name servers for the com domain. Notice the dot (.) at the end, this is what makes this a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). Let’s use these Name servers to query again.
Dig 2’nd query
Now we get the list of authoritative name servers for indianrail.gov.in(ns1.indianrail.gov.in and ns2.indianrail.gov.in). Now we need to query these name servers to get the IP-address of Indianraol.gov.in
Dig 3’rd query
And now in the Answer Section we can see that the Ip-address for indianrail.gov.in is 203.176..113.82
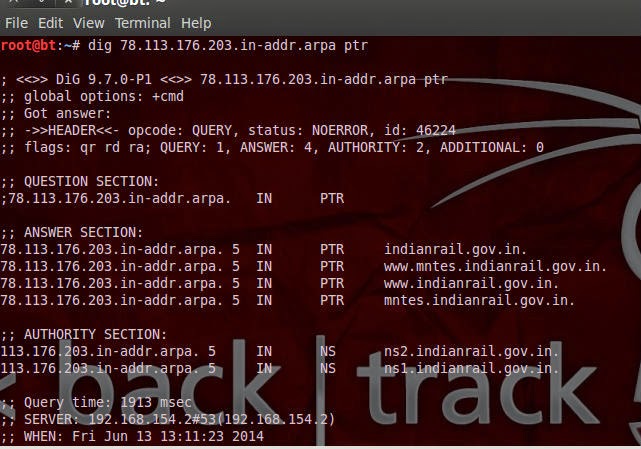
Reverse DNS Lookup- Performing Reverse DNS Lookup converts an IP-address into it’s hostname. For this we need to write the IP-address in reverse order (for e.g. 192.168.1.1 will be 1.1.168.192) and then append “.in-addr.arpa.” to it. Next we need to make a query for a PTR Record using DIG. Let’s make a DNS PTR query for 203.176.113.78, the command here would be “dig 78.113.176.203.in-addr.arpa PTR”
4 Dns ZONE transfer :-
For example google.com had ns1.google.com and ns2.gooogl.com are two name server related to google.com which handle the google.com request. So many big organization has one more name server in which one is master and second one is slave server. The Master server will provide the slave server with all the information it has. This is basically what is called a “Zone Transfer”. It’s like asking the nameserver “Give me everything you have A properly configured nameserver should only be allowed to serve requests of Zone transfer from other Nameservers of the same domain. However if the server is not configured properly it will serve all requests of Zone transfer made to it without checking the querying client. This leads to leakage of valuable information. DNS Zone transfer is sometimes referred through it’s opcode mnemonic AXFR.
Lets see an example of zone transfer by using tool fierce in backtrack machine .
5 Why is Zone transfer a Security Issue?
A zone transfer reveals a lot of information about the domain. This forms a very important part of the “Information Gathering” stage during a penetration test, vulnerability assessment etc. We can figure out a lot of things by looking at the dump.For e.g. we can find different subdomains. Some of them might be running on different servers.Those server may not be fully patched and hence be vulnerable.From this point, we can start thinking about Metasploit ,Nmap etc and do a full vulnerability assessment of the domain. Hence this kind of information increases our attack vector by a fair amount, an amount which cannot be ignored.
To protect your nameservers from leaking valuable information, one must allow zone transfer to other nameservers of the same domain only. For e.g. ns1.example.com should allow zone transfer to ns2.example.com only and discard all the other requests
6 Conclusion:-
DNS protocol is a very critical component of the Internet as it resolves IP-address into hostnames and makes life a lot easier for us. However, if the nameservers are not properly configured they might leak out the whole DNS server database to any malicious hacker. Even if the servers are properly configured, they can be brute forced to leak information about their mail servers, IP addresses, etc. It is therefore important to properly configure your DNS servers and be aware of the security issues with DNS.




This is a really informative knowledge, Thanks for posting this informative Information. Domain into IP tool
ReplyDeleteA DNS 'mail exchange' (MX) record guides email to a mail laborer. The MX record indicates how email messages should
ReplyDeletebe coordinated by the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP, the standard show for all emails).
Like CNAME records, an MX record ought to always point to another domain.
If you want to know that What Type Of Information Is Contained In A Dns Mx Record then visit this sit for more information:
What Type Of Information Is Contained In A Dns Mx Record?